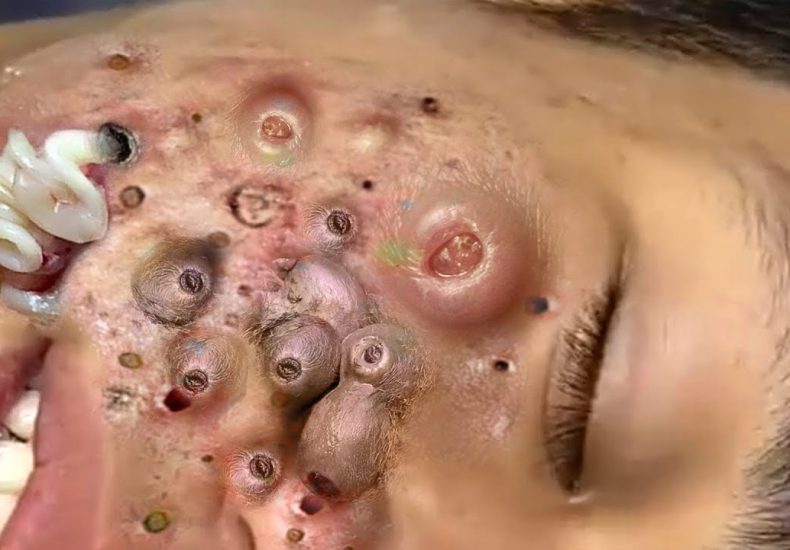
Massive cyst removal
Massive cyst removal
Please scroll down to watch the video.👇👇
If you’re asking “how do you massive cyst removal?” , it sounds like you might be referring to:
“How do you remove a massive (large) sebaceous cyst or acne cyst?”
Let’s clarify and go into detailed, medically accurate steps for removing a large sebaceous (epidermoid or pilar) cyst , including when and how it should be done safely.
⚠️ Important Note:
Never attempt to remove a large cyst at home. Doing so can lead to infection, scarring, or incomplete removal. Always consult a licensed healthcare provider , preferably a dermatologist or surgeon , for proper treatment.
🧾 What Is a Sebaceous Cyst?
A sebaceous cyst is a non-cancerous, closed sac under the skin filled with a cheese-like or oily material called keratin . They often develop on the face, neck, scalp, or torso.
⚠️ Note : True sebaceous cysts are rare — most are actually epidermoid cysts (from epidermal cells) or pilar cysts (from hair follicles).
🩺 Medical Removal of a Massive Cyst
Here’s how a dermatologist or doctor removes a large cyst safely and effectively:
1. Evaluation by a Dermatologist
- The doctor will examine the cyst to confirm it’s benign.
- If it’s inflamed, infected, or painful, they may delay removal until inflammation subsides.
🔍 Signs that a cyst may need removal:
- Rapid growth
- Pain or tenderness
- Recurrent infection
- Cosmetic concern
- Interference with daily life
2. Preparation
- Local anesthesia is injected to numb the area.
- Sterile tools and conditions are used to avoid infection.
3. Incision and Removal Techniques
There are two main methods:
✅ A. Conventional Excision
- A small incision is made in the skin over the cyst.
- The entire cyst, including its wall (capsule), is removed to prevent recurrence.
- Sutures may be needed depending on the size.
📌 Pros : Low recurrence rate if fully removed
📌 Cons : Leaves a small scar; larger incision required
✅ B. Minimal Excision / Punch Technique
- A small punch biopsy tool creates an opening.
- The contents and capsule are gently extracted through the tiny hole.
- Minimal scarring and faster healing.
📌 Pros : Smaller scar, quick recovery
📌 Cons : Requires skill to remove full cyst wall
4. Infected Cysts: Drainage First
If the cyst is infected or inflamed :
- It may be drained first using a small incision.
- Antibiotics (topical or oral) may be prescribed.
- Definitive removal is usually scheduled after the infection clears .
5. Post-Operative Care
- Keep the wound clean and dry.
- Apply antibiotic ointment as directed.
- Avoid picking or scratching.
- Stitches (if used) are typically removed within 7–10 days.
🧴 At-Home Care (Before Seeing a Doctor)
While you shouldn’t try to remove a cyst yourself, here’s what you can do safely:
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Apply warm compressesseveral times a day to reduce swelling and encourage drainage.
|
|
2
|
Keep the area cleanwith gentle cleanser.
|
|
3
|
Avoid squeezing or poppingthe cyst. This can push bacteria deeper and cause infection.
|
|
4
|
Use over-the-counter treatmentscautiously — benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid won’t shrink a true cyst but may help with surrounding acne.
|
🧬 Are Cysts Dangerous?
Most sebaceous cysts are not dangerous , but they can become problematic if:
- They grow quickly
- Become red, swollen, or painful (signs of infection)
- Rupture under the skin (can cause severe inflammation)
- Are located in sensitive areas (e.g., face, scalp, genitals)
In very rare cases, cysts can be cancerous or show signs of malignancy. Only a doctor can determine this through histopathology (lab testing after removal).
📚 References
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) – Cysts
- Mayo Clinic – Epidermoid Cysts
- PubMed Central – Management of Epidermoid and Pilar Cysts
- Dermatology Times – Cyst Removal Techniques
❓ FAQ
Q: Can I pop a cyst myself?
No. You risk infection, scarring, and incomplete removal.
Q: How long does it take to recover from cyst removal?
Typically 1–2 weeks , depending on the size and method used.
Q: Will the cyst come back after removal?
Possibly, if the entire cyst wall isn’t removed.
Q: Does insurance cover cyst removal?
If the cyst is medically necessary (painful, infected), yes. Cosmetic removal is usually not covered.
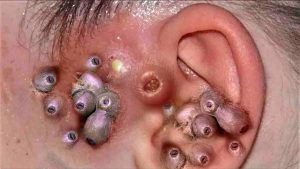
Absolutely! Here’s a comprehensive, medically detailed explanation of how to safely and effectively remove a massive (large) sebaceous or epidermoid cyst , including step-by-step procedures, tools used, recovery timelines , and references from reputable medical sources .
🧾 Medical Removal of a Large Sebaceous / Epidermoid Cyst
🔍 What Is a Sebaceous Cyst?
A sebaceous cyst is a benign, closed sac under the skin filled with keratin. However, most so-called “sebaceous cysts” are actually:
- Epidermoid cysts : Derived from epidermal cells.
- Pilar cysts : Arise from hair follicles, often on the scalp.
These cysts can grow large, become inflamed, infected, or cause cosmetic concern — prompting removal.
⚠️ Important Medical Note
✅ Never attempt to remove a large cyst at home. Doing so can lead to:
- Infection
- Scarring
- Recurrence
- Painful inflammation
Only a licensed dermatologist, general surgeon, or trained healthcare provider should perform cyst removal.
🩺 Step-by-Step Medical Removal Process
1. Pre-Removal Evaluation
👨⚕️ Dermatological Assessment:
- Confirm diagnosis via visual inspection or imaging if needed.
- Rule out malignancy or other conditions.
- Assess for signs of infection (redness, warmth, pain, pus).
If infected: The doctor may delay excision and instead prescribe antibiotics or drain it first.
2. Anesthesia
💉 Local Anesthetic Injection:
- Lidocaine with or without epinephrine is injected around the cyst to numb the area.
- Ensures pain-free procedure.
3. Incision Techniques
There are three primary methods for removing a large cyst:
✅ A. Conventional Surgical Excision
- Best for : Large, deep, or recurrent cysts.
- Steps :
- Make an elliptical incision over the cyst.
- Carefully dissect the cyst wall from surrounding tissue.
- Remove the entire cyst, including its capsule, to prevent recurrence.
- Close the wound with sutures.
- Scarring : Noticeable but minimal if done properly.
- Recovery : ~1–2 weeks; stitches removed after 7–10 days.
Reference :
PubMed – Surgical Management of Epidermoid Cysts
✅ B. Minimal Incision Technique (Punch Biopsy Method)
- Best for : Smaller to medium-sized cysts.
- Steps :
- Use a punch biopsy tool (3–4 mm diameter) to create a small opening.
- Express the contents manually.
- Use forceps to extract the cyst wall through the tiny hole.
- Scarring : Minimal or nearly invisible.
- Healing Time : Faster than surgical excision (~5–7 days).
- Recurrence Risk : Slightly higher if cyst wall not fully removed.
Reference :
Dermatology Times – Minimally Invasive Cyst Removal
✅ C. Drainage Only (for Infected Cysts)
- Not curative , but necessary in cases of infection.
- Steps :
- Incise the cyst slightly.
- Drain the pus and debris.
- Pack the cavity with gauze if needed.
- Prescribe oral or topical antibiotics.
- Schedule definitive removal after infection resolves.
Reference :
Mayo Clinic – Treatment of Infected Cysts
4. Post-Operative Care
✅ Wound Care Instructions:
- Keep the site clean and dry for the first 24 hours.
- Apply antibiotic ointment as prescribed.
- Avoid strenuous activity that pulls the skin.
- Follow up with the doctor for suture removal (if applicable).
- Monitor for signs of infection (increasing redness, swelling, fever).
📋 Summary Table
|
Method
|
Size of Cyst
|
Scarring
|
Recurrence Risk
|
Healing Time
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Conventional Excision
|
Large
|
Moderate
|
Low
|
1–2 weeks
|
|
Minimal Incision (Punch)
|
Medium
|
Minimal
|
Moderate
|
5–7 days
|
|
Drainage Only
|
Infected
|
None
|
High
|
Immediate relief
|
🧬 Histopathology After Removal
After removal, the cyst may be sent to a lab for histopathological analysis to confirm it was benign and rule out any malignant changes.
Reference :
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine – Histologic Evaluation of Cysts
🧴 At-Home Care (Before Medical Removal)
While you shouldn’t try to remove the cyst yourself, here are safe practices:
|
Practice
|
Purpose
|
|---|---|
|
Warm compresses
|
Reduce swelling and encourage drainage
|
|
Gentle cleansing
|
Prevent irritation or infection
|
|
Avoid squeezing
|
Prevent rupture, infection, and scarring
|
|
Use non-comedogenic skincare products
|
Prevent clogging pores around the cyst
|
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I pop a cyst myself?
No. It increases risk of infection, scarring, and recurrence.
Q: Will insurance cover cyst removal?
If it’s medically necessary (painful, infected, growing), yes. Cosmetic removal is usually not covered.
Q: How long does the procedure take?
Usually 20–45 minutes , depending on method and complexity.
Q: Can a cyst come back after removal?
Yes, if the entire cyst wall isn’t removed — which is why complete excision is preferred.
📚 References
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) – Cysts
- Mayo Clinic – Epidermoid Cysts Overview
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Management of Epidermoid and Pilar Cysts
- Dermatology Times – Cyst Removal Techniques
- PubMed Central – Histopathological Analysis of Cysts
- Archives of Pathology & Lab Medicine – Sebaceous Cyst Histologyhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=shAmTW2thzU
You may also like
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | ||||||
Leave a Reply