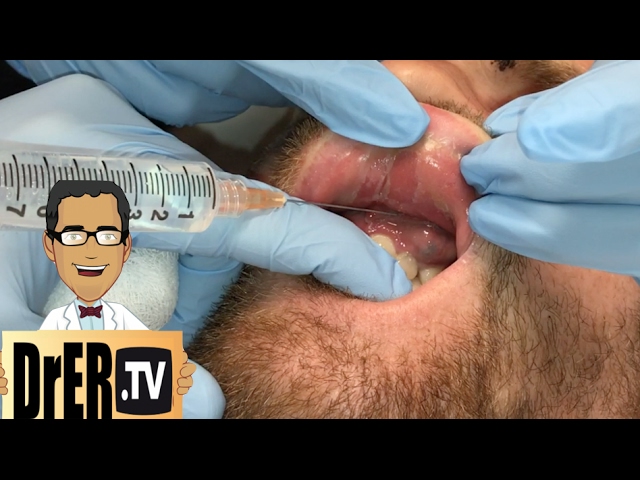
Get rid of pus in the tooth
Get rid of pus in the tooth
Please scroll down to watch the video.👇👇
Getting rid of pus in a tooth (usually caused by a dental abscess) requires prompt and professional dental treatment. Here’s a detailed guide on how it’s typically treated, along with references and clinical context:
🦷 What Is a Dental Abscess?
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection, usually at the root of a tooth or in the gums. It’s often extremely painful and can spread if left untreated.
⚠️ Symptoms of Tooth Pus (Abscess)
-
Severe toothache (throbbing or sharp)
-
Swelling in face or gums
-
Bad taste in the mouth
-
Fever
-
Sensitivity to hot/cold
-
Difficulty chewing or opening the mouth
✅ How to Treat It
1. See a Dentist Immediately
A dental abscess will not go away on its own. Professional treatment is essential to drain the pus and stop the infection from spreading.
🩺 Professional Dental Treatments
✅ A. Drainage of Abscess
-
The dentist makes a small incision in the gum or near the tooth to drain pus.
-
Saline or antiseptic may be used to rinse the area.
✅ B. Root Canal Treatment
-
If the infection is inside the tooth, a root canal removes the infected pulp, cleans the canal, and seals it.
-
This saves the natural tooth in many cases.
✅ C. Tooth Extraction
-
If the tooth is too damaged, it may be removed to prevent further spread of infection.
✅ D. Antibiotics
-
Prescribed to kill bacteria, especially if the infection has spread beyond the abscess.
-
Common choices: Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, or Clindamycin (if allergic to penicillin).
🏠 Home Care (While Waiting for Treatment)
These do NOT cure the infection but may help manage pain temporarily:
-
Rinse with warm salt water (3–4 times/day)
-
Cold compress to reduce facial swelling
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen or acetaminophen)
❗️Do Not:
-
Try to pop or drain the abscess yourself
-
Apply aspirin directly to gums or teeth
📚 References:
-
Mayo Clinic:
-
American Dental Association (ADA): Root Canal Therapy
-
NHS UK:
Treating a dental abscess—a localized collection of pus due to bacterial infection—requires prompt professional dental care. While home remedies can offer temporary relief, they do not address the underlying infection. Here’s a detailed overview:
🦷 Understanding Dental Abscesses
A dental abscess typically forms when bacteria invade the dental pulp through cavities, cracks, or gum disease, leading to pus accumulation. If left untreated, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues and even enter the bloodstream, posing serious health risks.
🩺 Professional Treatment Options
1. Incision and Drainage
For abscesses that are easily accessible, a dentist may perform an incision to drain the pus, relieving pressure and pain. In some cases, a small rubber drain is placed to keep the area open for continued drainage.
If the tooth is salvageable, a root canal procedure is performed to remove the infected pulp, clean the canal, and seal it to prevent re-infection. This treatment preserves the natural tooth structure.
3. Tooth Extraction
When the tooth is severely damaged and cannot be restored, extraction is necessary to prevent the spread of infection. Post-extraction, the area is cleaned to remove any remaining infectious material.
4. Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotics may be prescribed if the infection has spread beyond the abscessed area or if the patient has a weakened immune system. Common antibiotics include amoxicillin or clindamycin for those allergic to penicillin. However, antibiotics are not a substitute for dental procedures and are used adjunctively.
🏠 Home Care Measures (Temporary Relief)
While awaiting dental treatment, the following can help manage symptoms:
-
Saltwater Rinse: Mix 1/2 teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth to reduce inflammation and discomfort.
-
Cold Compress: Apply a cold pack to the affected area externally to alleviate pain and swelling.
-
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Use medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to manage pain.
Important: These measures do not cure the infection. Avoid attempting to drain the abscess yourself, as this can worsen the infection.
⚠️ Potential Complications of Untreated Abscesses
Neglecting a dental abscess can lead to severe complications, including:
-
Spread of Infection: To adjacent teeth, jawbone, or other facial structures.
-
Systemic Infection: Bacteria entering the bloodstream can cause sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
-
Airway Obstruction: Severe swelling can impede breathing.
🛡️ Preventive Measures
-
Maintain Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily, floss regularly, and use antiseptic mouthwash.
-
Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist every six months for cleanings and examinations.
-
Address Dental Issues Promptly: Treat cavities, gum disease, or tooth injuries early to prevent abscess formation.
-
Leave a Reply